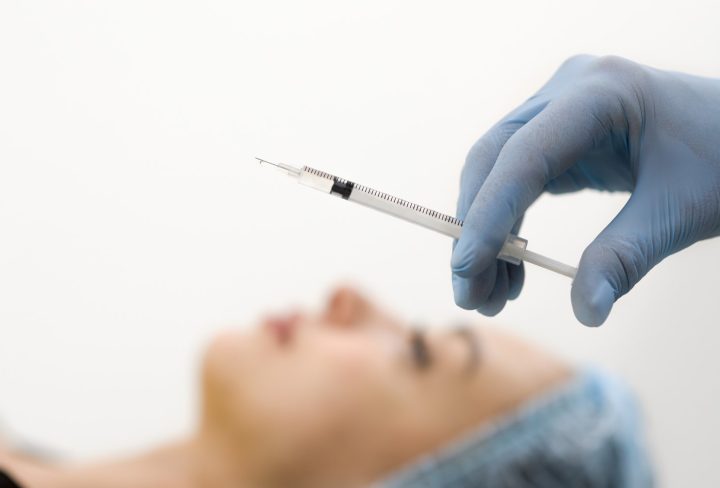
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure commonly used to evaluate suspicious or abnormal tissues or masses in the body. It involves extracting a small sample of cells or tissue using a thin needle for further examination under a microscope. This article aims to provide patients with a better understanding of FNA biopsy, including its purpose, procedure, benefits, and what to expect.
What is FNA Biopsy and Why is it Performed?
FNA biopsy is performed to obtain a sample of cells or tissue from a suspicious or abnormal area in the body. It helps in diagnosing various conditions, including:
- Cancer: FNA biopsy can determine if a mass or tumor is cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). It aids in identifying the type and stage of cancer, guiding treatment decisions.
- Infections: FNA biopsy can help identify the presence of infectious organisms, such as bacteria or fungi, in swollen lymph nodes or other infected areas.
- Inflammatory Conditions: It can assist in diagnosing certain inflammatory conditions, such as granulomas or autoimmune diseases.
The FNA Biopsy Procedure:
- Preparation: No special preparation is usually required for an FNA biopsy. However, inform your healthcare provider about any medications, allergies, or bleeding disorders.
- Local Anesthesia: The procedure is typically performed with local anesthesia to numb the area where the needle will be inserted. This helps minimize discomfort during the biopsy.
- Needle Insertion: Using imaging guidance, such as ultrasound or CT scan, the healthcare provider will insert a thin needle into the target area. You may feel slight pressure or a brief pinch at the needle insertion site.
- Sample Collection: The needle is gently moved back and forth to obtain a sample of cells or tissue. Multiple samples may be collected from different areas within the same lesion to ensure accuracy.
- Needle Removal: Once the sample is obtained, the needle is removed, and slight pressure may be applied to the biopsy site to prevent bleeding.
- Post-Procedure Care: Following the procedure, you may experience mild bruising, soreness, or minimal bleeding at the biopsy site. Applying a clean bandage and avoiding strenuous activities can help promote healing.
Benefits of FNA Biopsy:
- Minimally Invasive: FNA biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure that requires only a thin needle, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster recovery compared to surgical biopsies.
- Accurate Diagnosis: FNA biopsy provides valuable information to aid in the diagnosis of various conditions, enabling timely and appropriate treatment planning.
- Rapid Results: The samples obtained through FNA biopsy are usually sent to a pathology laboratory for analysis. Depending on the facility, results can be available within a few days.
- Guidance for Treatment: The information obtained from FNA biopsy helps healthcare providers determine the most suitable treatment options, such as surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or close monitoring.
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a safe and effective diagnostic procedure that provides important information about suspicious or abnormal tissues in the body. It aids in diagnosing conditions, including cancer, infections, and inflammatory diseases. With its minimally invasive nature, accuracy in diagnosis, and rapid results, FNA biopsy plays a critical role in guiding appropriate treatment decisions. If you have any concerns or questions about the procedure, consult your healthcare provider, who will provide specific guidance based on your individual case.